Patello-femoral pain syndrome is felt as pain in your knee that can be hard to localise to one spot. It normally feels like the whole knee, the front of the knee or the front-inside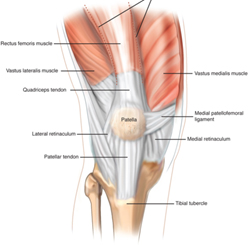 of your knee.
of your knee.
The patella is your knee cap and the femur is your thigh bone so patella-femoral pain syndrome is pain by the knee cap and thigh bone joint.
PFPS usually occurs when the muscles in your thigh aren’t all as strong as each other. PFPS happens when the muscles on the outside of your thigh are stronger than the ones on the inside. This means your knee cap may get pulled more towards the outside of your knee than it should and so may cause pain especially when you bend your knee and your knee cap comes close to your thigh bone.
PFPS is often felt most when climbing stairs or during exercise that involves repeatedly bending your knee. The pain may also be present after sitting with your knees bent for extended periods of time such as after watching a movie. The pain may be worse on certain activity surfaces or with different levels of activity intensity. PFPS pain may start gradually and worsen over time.
People who have flat feet or feet that function like they are flat are more likely to get PFPS as the leg muscles don’t work like they should because the foot isn’t working like it should. This means that to treat PFPS you need to correct the foot function and structure as well as strengthen the appropriate thigh muscles.
Treatment from home:
- Ice your knee regularly for 5-10 minutes at a time
- Avoid activities that aggravate the pain
- Do all exercises your podiatrist recommends
Treatment from your podiatrist may include:
- Physical examination to determine which muscles are weak
- Biomechanical assessment to assess your foot structure and function
- Taping and/or orthotics to improve your foot function so that the leg muscles can function better
- Footwear advice
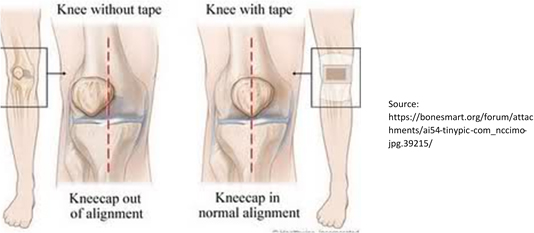
- Knee taping/bracing to relieve pain, assist in correct patella/knee cap alignment and encourage appropriate muscle balance
- Exercises such as squats to strengthen weak muscles
- Rehabilitation advice

Comments are closed.